Behavioral nudges have emerged as an effective tool for encouraging healthier food choices in educational institutions. A specific type of nudge, known as convenience nudges, simplifies access to healthier options, leading to more sustainable dietary habits. This blog examines key studies highlighting their impact.
1. UCLA Study: Menu Reordering for Low-Carbon Food Choices
A field study conducted at UCLA in 2021 tested the impact of convenience nudges by reordering menu items based on their carbon footprint. Two interventions were implemented:
- First Intervention: Menu items were listed from the highest (harmful) to the lowest (healthiest) carbon footprint.
- Second Intervention: The order was reversed, with low-carbon options placed at the top.
The results, involving over half a million menu selections, demonstrated a significant shift in student choices:
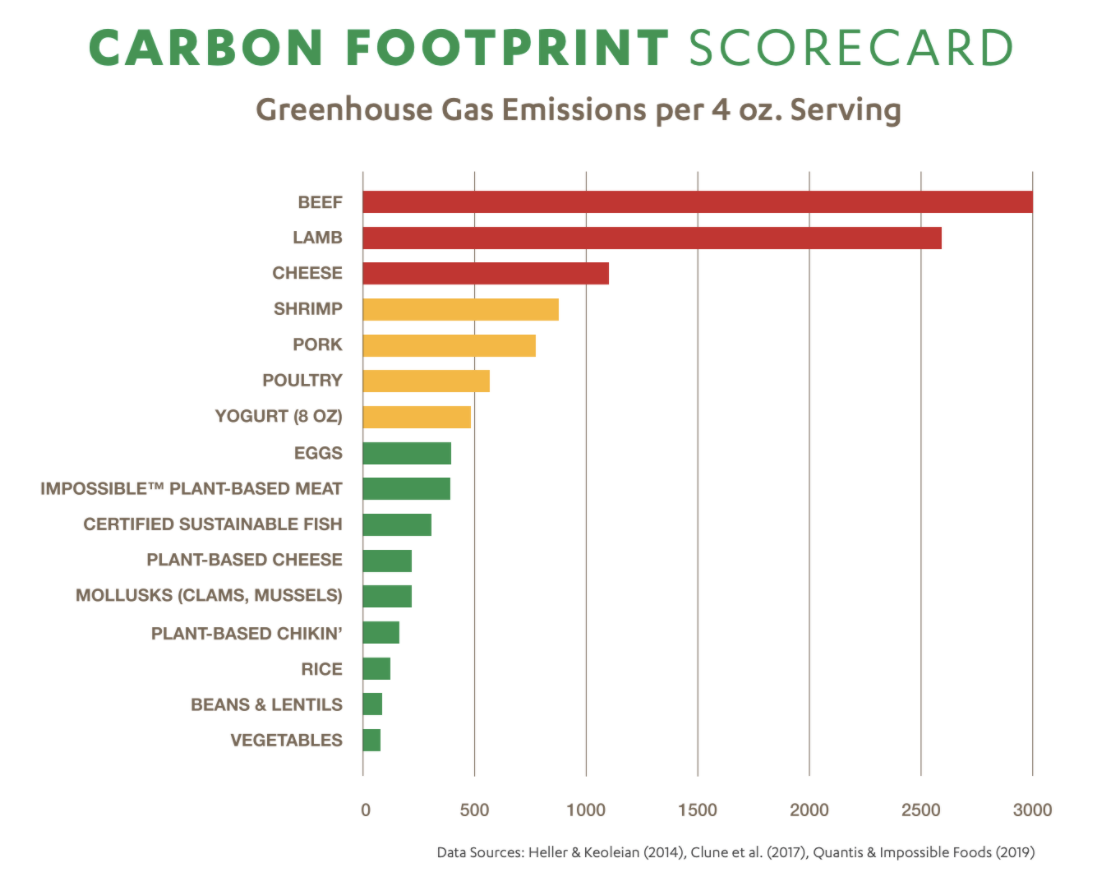
- Low-carbon food consumption increased from 46.2% to 53.8% between the first and second interventions.
- While beef consumption rose slightly during the second intervention, this anomaly was attributed to a national trend of increased beef consumption in 2021.
This experiment highlights the success of convenience nudges in driving healthier food choices by reducing the effort required to select them.
2. Midwestern Elementary School Study: Sliced Apples as a Nudge
A similar nudge intervention in a rural Midwestern school explored how slicing apples affected student consumption habits. Key findings included:
- 27.7% increase in apple consumption during the intervention period.
- Reduction in food waste: Apple waste decreased from 81% to 71%, saving an average of $0.0318 per apple.
This study also demonstrated cost-effectiveness:
- A one-time investment of $299 in an apple slicer could be offset by reduced food waste and increased efficiency.
- Sliced apples, being easier to eat, made the healthy choice more accessible, promoting better eating habits.
Challenges and Considerations
While these studies highlight the potential of convenience nudges, challenges remain:
- Lack of Control Groups: The Midwestern study lacked a control group, limiting the ability to isolate the nudge’s impact.
- Cultural and Regional Factors: Behavioral nudges might not produce uniform results across diverse settings.
Despite these limitations, the studies strongly support the effectiveness of convenience nudges in increasing the demand for healthier food options in schools.
Conclusion
Convenience nudges serve as a practical, cost-effective strategy for improving dietary habits and reducing environmental impact in educational institutions. Whether it’s reorganizing menus or slicing apples, small adjustments can make healthy choices more appealing and accessible.